

Appendix E. An Introduction to Disk Partitions
113
E.1.4.3.2. Resize the existing partition
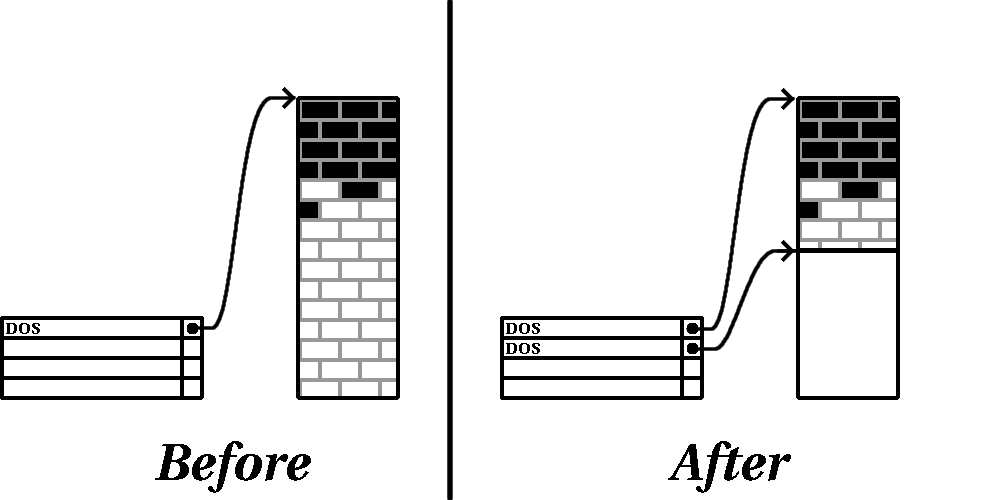
Figure E 12, shows the actual resizing process. While the actual result of the resizing operation varies
depending on the software used, in most cases the newly freed space is used to create an unformatted
partition of the same type as the original partition.
Figure E 12. Disk Drive with Partition Resized
It is important to understand what the resizing software you use does with the newly freed space, so
that you can take the appropriate steps. In the case we have illustrated, it would be best to simply
delete the new DOS partition and create the appropriate Linux partition(s).
E.1.4.3.3. Create new partition(s)
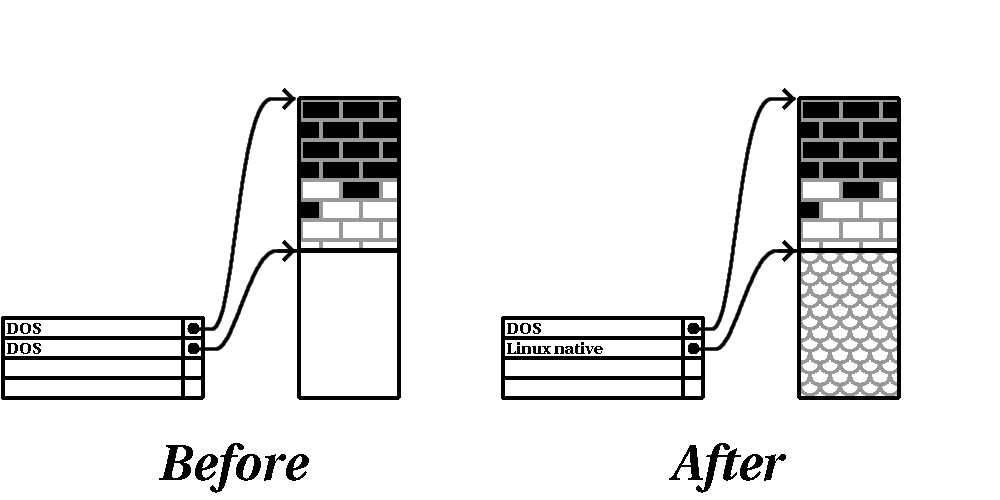
As the previous step implied, it may or may not be necessary to create new partitions. However, unless
your resizing software is Linux aware, it is likely you will need to delete the partition that was created
during the resizing process. Figure E 13, shows this being done.
Figure E 13. Disk Drive with Final Partition Configuration
Note
The following information is specific to x86 based computers only.
As a convenience to Red Hat Linux users, the DOS
fips
utility is included on the Red Hat Linux/x86
CD 1 in the
dosutils
directory. This is a freely available program that can resize FAT (File Alloca
tion Table) partitions.
Warning
Many people have successfully used fips to resize their hard drive partitions. However, because
of the nature of the operations carried out by fips and the wide variety of hardware and software
footer
Our partners:
PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor Best Web Hosting
Java Web Hosting
Inexpensive Web Hosting
Jsp Web Hosting
Cheapest Web Hosting
Jsp Hosting
Cheap Hosting
Visionwebhosting.net Business web hosting division of Web
Design Plus. All rights reserved


