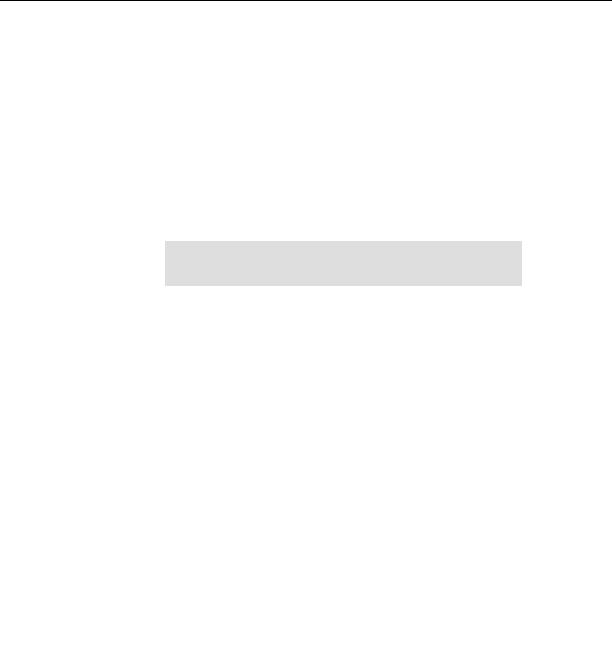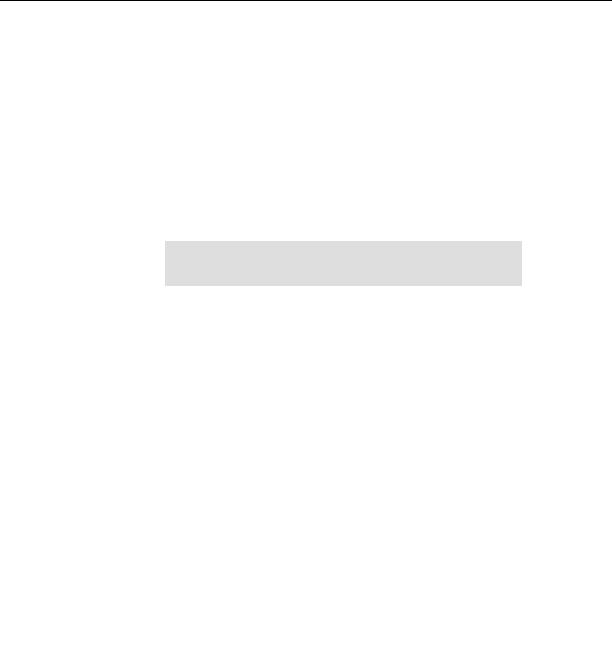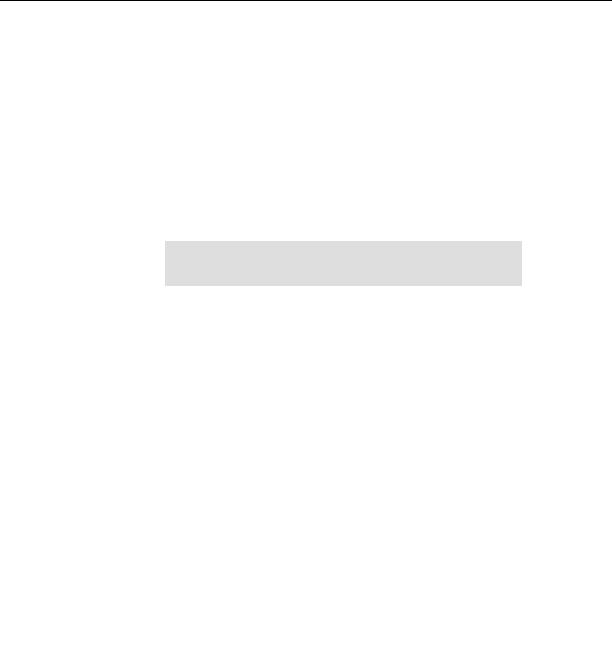
/dev/hda5 /scr auto noauto,user 0 0
/dev/hda2 swap swap pri=42 0 0
......
/dev/fd0 /media/floppy subfs fs=floppyfss,procuid,nodev,nosuid,sync 0 0
//itsont05/data
/shares/data_g smbfs
credentials=/root/.credentials
0
0
This works fine unless the Windows file share uses non standard characters. In
contrast to UNIX like operating systems, Windows allows you to use space
characters or even German umlauts in the names of file shares. You may run
into problems in the case where the Windows file shares contain special
characters. For example, the /etc/fstab file uses the space character as a
delimiter, so if a share contains a space, it will take the following string as a
mount point. So, while mounting the project data file share, the mount
command complains about several errors in the fstab file, as it tries to use data
as a mount point.
Tip:
When mounting Windows file shares in a Linux file system, it is very
reasonable to check the names of the shares for special characters.
Renaming them UNIX compliant can save a lot of time and annoyance.
Thus we had to use another way of mounting the file share, and we decided to
extend the /etc/rc.local file with the corresponding
smbmount
commands.
Modifications to rc.local are shown in Example 6 8.
Example 6 8 Extended rc.local file
#!/bin/sh
#
# This script will be executed *after* all the other init scripts.
# You can put your own initialization stuff in here if you don t
# want to do the full Sys V style init stuff.
touch /var/lock/subsys/local
#mounting windows file shares
smbmount //itsont05/data /shares/data_g o credentials=/root/.credentials,
gid=ITSOAUSNT+Domain\ Users,dmask=0775
smbmount //itsont02/"project data" /shares/projectdata_e o credentials=/root/.credentials,
gid=ITSOAUSNT+Domain\ Users,dmask=0775
If using file shares with special characters here, it is necessary to put them in
quotation marks, as shown in the last line of the example above. The gid and
dmask options of the
smbmount
command are used to ensure that the
permissions are set in the right way for the Linux directories in which the shares
are mounted. If they are left out, users would not have write permissions
122
Linux Client Migration Cookbook A Practical Planning and Implementation Guide for Migrating to Desktop
footer
Our partners:
PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor Cheap Web Hosting
JSP Web Hosting
Ontario Web Hosting
Jsp Web Hosting
Cheapest Web Hosting
Java Hosting
Cheapest Hosting
Visionwebhosting.net Business web hosting division of Vision Web Hosting Inc.. All rights reserved