CIDR Address Allocation Example
For this example, assume that an ISP owns the address block
200.25.0.0/16. This block represents 65,536 (216) IP addresses (or 256
/24s).
The ISP wants to allocate the smaller 200.25.16.0/20 address block,
which represents 4,096 (212) IP addresses (or 16 /24s).
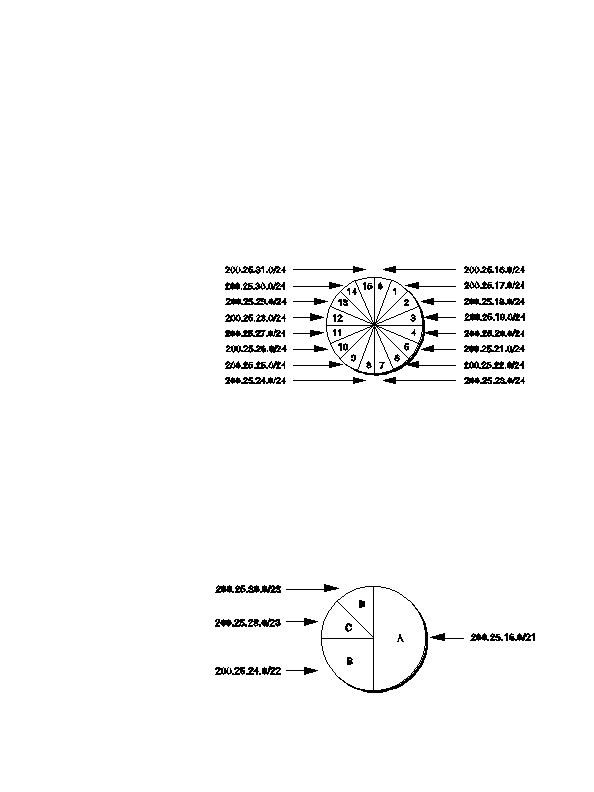
Address Block 11001000.00011001.00010000.00000000 200.25.16.0/20
In a classful environment, the ISP is forced to use the /20 as 16 individ
ual /24s.
F I G U R E 3 0 . S l i c i n g t h e P i e C l a s s f u l E n v i o r n m e n t
However, in a classless environment, the ISP is free to cut up the pie
any way it wants. It could slice the original pie into pieces (each one
half of the address space) and assign one portion to Organization A,
then cut the other half into two pieces (each one fourth of the address
space) and assign one piece to Organization B, and then slice the
remaining fourth into two pieces (each one eighth of the address space)
and assign them to Organization C and Organization D. Each of the orga
nizations is free to allocate the address space within its Intranetwork
as desired. This example is illustrated in Figure 31.
F I G U R E 3 1 . S l i c i n g t h e P i e C l a s s l e s s E n v i o r n m e n t
3 5
footer
Our web partners:
Inexpensive
Web Hosting
Jsp Web Hosting
Jsp Web Hosting
Cheapest Web Hosting
Java Web Hosting
Quality Web Templates
Dreamweaver Web Templates
Frontpage Web Templates
Jsp Web Hosting
Cheapest Hosting
Cheapest Web Hosting
Java Web Hosting
Tomcat Web Hosting
Quality Web Hosting
Best Web Hosting
Java Web Hosting
Visionwebhosting.net Business web hosting division of Vision Web Hosting Inc.. All rights reserved

